All About Malware - Overview

Malware stands for malicious software, meaning software that can be used to cause harm to the host computer. Malware is a broad term that refers to a variety of malicious programs. The most common types of malware as below :
- Virus
- Adware
- Bot
- Ransomware
- Rootkit
- Spyware
- Trojan Horse
- Worm
- Spam
- Keylogger
- Backdoors
- Phishing
Virus
A computer virus is malicious computer program that replicates by copying itself to another program or computer boot sector which changes the way computer works. A virus can be spread by opening an email attachment, clicking on an executable file, visiting an infected website, connecting removable storage device or viewing an infected website advertisement.
Adware
Adware is unwanted software designed to throw advertisements up on your screen, redirect your search requests to advertising websites and collect marketing-type data about you. The ads are delivered through pop-up windows or bars that appear on the program's user interface. Adware is commonly created for computers, but may also be found on mobile devices.Bot
A bot is an automated program that runs over the Internet. Some bots run automatically, while others only execute commands when they receive specific input. There are many different types of bots, but some common examples include web crawlers, chat room bots, and malicious bots. While most bots are used for productive purposes, some are considered malware, since they perform undesirable functions.Ransomware
Ransom malware, or ransomware, is a type of malware that prevents users from accessing their system or personal files and demands ransom payment in order to regain access. Today, ransomware authors order that payment be sent via crypto currency or credit card. Ransomware controls over your computer, threatens you with harm, usually by denying you access to your data.Rootkit
The term rootkit is a connection of the two words "root" and "kit". A rootkit is one of the most difficult types of malware to find and remove. Once a rootkit installs itself on your computer, it will boot up at the same time as your PC. On top of that, by having administrator access, it can track everything you do on the device, scan your traffic, install programs without your consent, hijacker your computer’s resources or enslave it in a botnet.Spyware
Spyware is software that is installed on a computing device without the end user's knowledge. It’s actually a generic term for malicious software that infects your PC
or mobile device and gathers information about you, your browsing and
Internet usage habits, as well as other data. That includes capturing keystrokes, screen shots, authentication
credentials, personal email addresses, web form data, Internet usage
information, and other personal information, such as credit card
numbers.
Trojan Horse
Trojans contain malicious code that when triggered, cause loss, or even theft, of data. Trojans can be Appoint by hackers trying to gain access to users systems. Users are typically tricked by some form of social engineering into loading and executing Trojans on their systems. Once Trojan is activated, it can enable cyber-criminals to spy on you, steal your sensitive data, and gain backdoor access to your system. These actions can include Deleting data, Blocking data, Modifying data, Copying data, Disrupting the performance of computers or computer networksWorm
Worm is self-replicating malware that duplicates itself to spread to uninfected computers. It is a type of virus which does not alter any files on your machine instead worms can still cause havoc by multiplying so many times that they take up all your computer's available memory or hard disk space. If a worm consumes your memory, your computer will run very slowly and possibly even crash. If the worm affects your hard disk space, your computer will take a long time to access files and you will not be able to save or create new files until the worm has been eradicated.Spam
Irrelevant or unsolicited messages sent over the Internet, typically to a large number of users, for the purposes of advertising, phishing, spreading malware, etc. Fraudulent spam also comes in the form of phishing emails, which are emails disguised as official communication from banks, online payment processors or any other organizations a user may trust. Users should avoid opening spam emails and never respond to them or click on links in the messages. Spam email may also deliver other types of malware through file attachments or scripts, or contain links to websites hosting malware.Keylogger
Keyloggers are used as a spyware tool by hackers to steal personally information , login credentials and sensitive important data. Keylogger recorders may also be used by organisations to observe employees computer activities, parents to supervise their children's internet usage, users to track possible unauthorized activity on their devices or law enforcement agencies to analyze incidents involving computer use.Backdoors
A backdoor is a malware type that bypassed security mechanism undetectably to access a computer or its data. As a result, remote access is granted to resources within an application, such as databases and file servers, giving permission to remotely issue system commands and update malware.Phishing
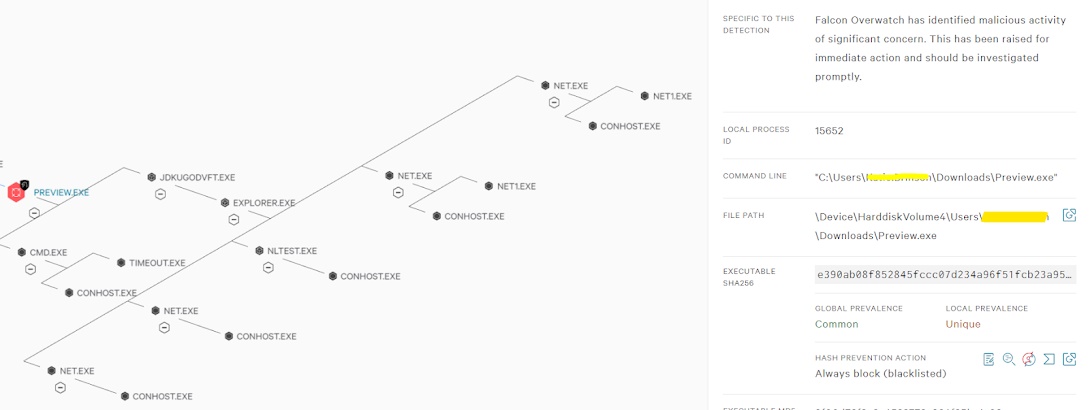
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which a targets are contacted by email, telephone or text message by someone posing as a legitimate source to ask to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers.Malware Analysis
Malware analysis is the art of Exploring malware to understand how it
works, how to identify it, and how to defeat or eliminate it. The Goals of malware Analysis to respond to a network intrusion system like Exactly what happened, Ensure you’ve located all infected machines and
files,How to measure and contain the damage, Find signatures for intrusion detection systems.
There are two fundamental approaches to malware analysis: static and dynamic. Static analysis involves examining the malware without running it. Dynamic analysis involves running the malware. Both techniques are further categorized as basic or advanced.
Advance Static: Advanced static analysis consists of reverse-engineering the malware’s internals by loading the executable into a disassembler and looking at the program instructions in order to discover what the program does.
Basic Dynamic : Basic dynamic analysis techniques involve running the malware and observing its behavior on the system in order to remove the infection, produce effective signatures, or both.
Advance Dynamic : Advanced dynamic analysis uses a debugger to examine the internal state of a running malicious executable. Advanced dynamic analysis techniques provide another way to extract detailed information from an executable.
Why Malware Analysis?
Malware Detection is Done by different means like Signature Based, Rule Based , Behavioral Blocking, Sand box and pattern matching. however, we can perform this using different tools and utilities. below are the few important utilities used for Malware Analysis :
Few terminologies to be remember while performing Malware Analysis:
Types of Malware Analysis
There are two fundamental approaches to malware analysis: static and dynamic. Static analysis involves examining the malware without running it. Dynamic analysis involves running the malware. Both techniques are further categorized as basic or advanced.
Basic Static : Basic static analysis consists of examining the executable file without viewing
the actual instructions.also confirms whether a file is malicious, provide information about its functionality.
Advance Static: Advanced static analysis consists of reverse-engineering the malware’s internals by loading the executable into a disassembler and looking at the program instructions in order to discover what the program does.
Basic Dynamic : Basic dynamic analysis techniques involve running the malware and observing its behavior on the system in order to remove the infection, produce effective signatures, or both.
Advance Dynamic : Advanced dynamic analysis uses a debugger to examine the internal state of a running malicious executable. Advanced dynamic analysis techniques provide another way to extract detailed information from an executable.
Why Malware Analysis?
- To understand the Potential of the malware
- Determine how the malware works
- Evaluate the intrusion damage
- Identify indicators that will helps us determine other infected machine by the same malware and the level of infection in the network
- Help us identify if the malware is exploiting any vulnerability or on how it is persisting on the system
- Determine the nature & Motivation of the malware
- To understand who is targeting & how good they are.
- To understand what information did they steal.
Malware Detection is Done by different means like Signature Based, Rule Based , Behavioral Blocking, Sand box and pattern matching. however, we can perform this using different tools and utilities. below are the few important utilities used for Malware Analysis :
Few terminologies to be remember while performing Malware Analysis:
- Strings
- Hash
- Packed and Obfuscated Malware
- PE file Format (Headers and Section)
- Linked Libraries and Functions
- Assembly Language
Tools for Static Analysis :
- Dependancy Walker
- Resource Hacker
- PEview
- File Analyzer
- Hashcalc
- RegRipper
- HxD
- Virus Total
- Regshot
- PEiD
Tools for Dynamic Analysis :
- ProcessExplorer
- RegShot
- ApateDNS
- Netcat
- Wireshark
- INetSim
- IDA Pro
- Cuckoo Sandbox
- OllyDbg
- WinDbg
- Muninn
- DAMM
- FindAES
- Volatility
- Procmon
Stay Tuned for Profound understanding of Malware Analysis in my next Blog.....







Comments
Post a Comment