Threat Hunting Basics - Part 7
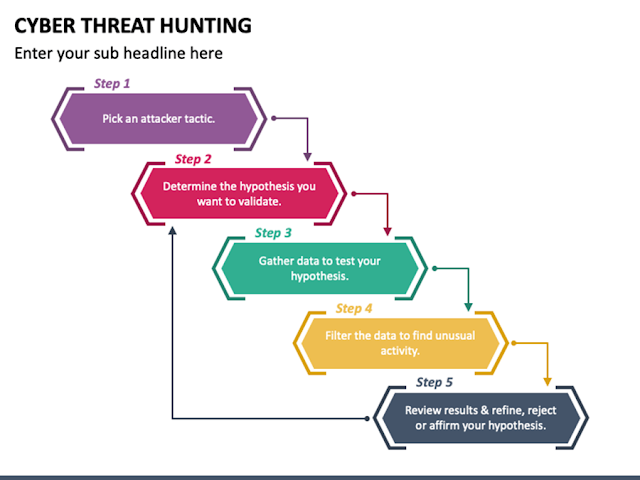
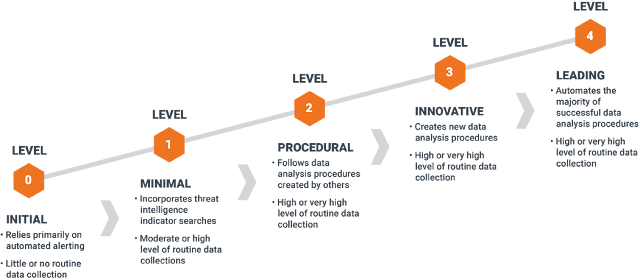
Threat hunting Report The below Metrics should be included in the Threat hunting report but not limited to it. Hypothesis Attack Vector Description Scope Data Sources Analysis Techniques Findings Security Recommendations Timestamps Conclusion References Let's understand what should be included in the above pointers : Hypothesis Threat hunting is primarily hypothesis-driven. This proposed explanation is then used as a starting point for further investigation. Attack Vector Attack vectors are the ways an attacker can breach sensitive data or compromise an organization. Cyber kill chain Step Attack Type & TTP ID Attack Description Description Explanation of Hypothesis and malicious observed behavior Scope Defining the scope and hypotheses of the engagement is the initial step of a Proactive Threat Hunting activity. We will work alongside the blue team to define the scope, whether it is organization-wide, limited scope or to address a specifically targeted threat. Dep...